RFID - RAIN

Benefits
Every industrial application presents a unique set of challenges and demands to a radio frequency identification (RFID) solution. By understanding the unique capabilities each system offers, companies can select the best option for their particular need.
RAIN in more detail
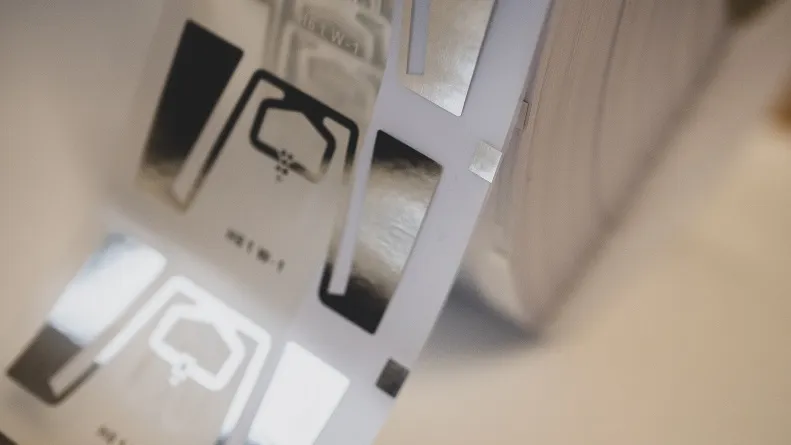
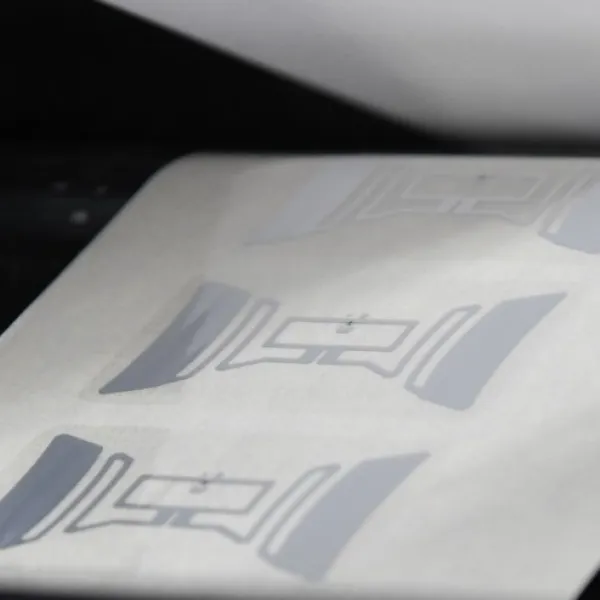
RAIN ICs combine very small size with huge performance. The latest generation of RAIN IC’s are less than 0,1 square mm with over half a million chips on a 12 inch wafer. Despite their size, they offer a lot of performance. Depending on the antenna design, tags can be read within a distance in the area of 20 meters. They can also be read in bulk at a speed of up to 1000 per second.
RAIN applications range from Retail to Courier Services to Logistics and Asset Management. RAIN is really the technology of choice with only two limitations.
- The first is that a dedicated reader is required. That is a major difference with NFC, where the reader is integrated into smartphones.
- The second limitation is built-in security. Although RAIN is working on more security features, NFC offers a lot more in this area.
Some very large RAIN applications are in Retail (Walmart, C&A, H&M, Zara, Decathlon and many others) where the main application is in-store inventory and automated check-out. Furthermore RAIN is used for Courier Services (ie: UPS), Airlines (Delta, Air France and many airports) and in the Pharmaceutical market.